Your products are beyond excellence, and distributors have the determination to succeed. That means the foundation of your MLM business is rock solid. This solid foundation deserves an exceptional superstructure, only possible with a robust MLM shipping system.
So, buckle up, and let’s explore the MLM shipping system in detail, its types, its core features, and optimization strategies.
This Article Contains:
What is an MLM Shipping System?
The MLM shipping system consists of tools, processes, and rules that guide MLM product shipping from the manufacturing plant to the buyer or distributor. It takes care of storage, packaging, and delivery of MLM products.
Unlike the traditional shipping system, the MLM shipping system is more complex and sensitive, as the system needs to take care of delivery to customers as well as distributors.
When you sell products through distributors, not only your reputation but also your distributors’ reputation is at stake as well. If the product is delayed or comes with high delivery charges, it can have a negative impression on the end customer.
Therefore, the MLM shipping system must ensure timely and cost-effective delivery. Apart from that, there are several other features of an MLM shipping system, which we will discuss in the upcoming sections.
For now, let’s understand how it is different from traditional shipping.
How does the modern MLM shipping system differ from traditional e-commerce shipping?
While both e-commerce and MLM businesses rely on shipping for delivering products, the underlying logistics differ significantly. The traditional shipping system is quite straightforward, where the products are shipped from the warehouse to customers, whereas the MLM shipping infrastructure is much more complex, with products shipped to customers as well as distributors.
| Aspect | Traditional E-commerce Shipping | Modern MLM Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Order Origin & Workflow | Orders initiated by customers (B2C) via online storefront; linear pipeline (warehouse → customer). | Orders via storefront or distributor dashboard; supports B2C & B2B (bulk distributor procurement); requires commission integration. |
| System Integration & Data Sync | Integrates with ERP, WMS, and payment gateways; one-directional data flow for efficiency. | Multi-layered integration with ERP, WMS, MLM back-office (genealogy, commissions, distributor portals); real-time, event-driven sync (e.g., pulling back commissions on returns). |
| Inventory Distribution Topology | Centralized or hub-and-spoke model; stock tracked at warehouses only. | Multi-tier (central DC → regional hubs → distributors → customers); includes distributor stock; uses Multi-Echelon Inventory Optimization for demand prediction and balancing. |
| Carrier Management & Logistics | Mostly parcel-level; carrier chosen per order; optimized for cost, speed, SLA adherence. | Supports both parcel (LTL) & bulk (FTL) shipments; multi-layer carrier orchestration (warehouse → distributors/customers/hubs); automated load-building & cost optimization. |
| Regulatory & Compliance | Focused on taxes, customs, invoices, and PCI-DSS compliance. | Includes all e-commerce compliance + MLM-specific rules (proof of sale validation, anti-inventory loading, genealogy-linked payouts, immutable shipment logs, chain-of-custody tracking). |
Due to the added complexity, the MLM shipping system necessitates numerous additional features, including commission tracking, enhanced compliance management tools, and network management capabilities.
On that note, let’s discuss the differences in detail:
Order Origin and Workflow Architecture
In traditional e-commerce, orders are initiated by customers through the business’s digital storefront or e-commerce website, making the transaction B2C.
It follows a linear pipeline where the initiated order is first reflected in the order management system. From here, the order is processed and shared with the preferred warehouse based on its order location and product availability.
Once the warehouse ships the order, it’s tracked using the transport management system, which handles the product status from the warehouse to delivery.
However, the modern MLM system has multiple actors, requiring multi-directional order routing. The order can be placed through the digital storefront or distributor’s dashboard. An integrated MLM shipping system then identifies whether it's a single B2C transaction or bulk procurement by a distributor. Based on that, the order is placed in the relevant pipeline.
For direct-to-customer orders, the same pipeline is followed as traditional shipping. However, when a distributor is involved, the workflow architecture depends on whether the business follows a direct sales commission or a retail commission method.
In the case of direct sales commission, the transaction is made by the end purchaser through the distributor’s exclusive link. Therefore, the MLM shipping system must be connected to commission management software. So, whenever a sale is made, the predefined commission gets reflected in the distributor’s dashboard.
When there’s a bulk procurement by the distributor, it’s considered a B2B transaction. Here, the shipping system + commission management tool integration define the wholesale pricing depending on the distributor’s rank and number of units. It also adds the required taxes, duties, and tariffs before approving the order.
The order is shipped from the warehouse to the distributor rather than the end user. Sales made to the end users via a distributor are typically the distributor’s responsibility. However, whenever a distributor reports a sale in their commission management system, it gets reflected in the network marketing shipping system.
So, the requirement of integration between the shipping system and the commission management system is the major difference-maker, which brings us to our next point.
System Integration and Data Synchronization
In a traditional e-commerce environment, the shipping system is integrated with the following:
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software for financial/accounting synchronization
WMS (Warehouse Management System) for inventory tracking
A payment gateway to facilitate transactions
The data synchronization is comparatively linear, where all the information flows in one direction: from the payment gateway to the shipping system to WMS to ERP. The overarching objective is transactional efficiency and compliance with delivery SLAs (Service-Level Agreements), with minimal dependencies beyond order-to-cash workflows.
As mentioned earlier, MLM shipping is much more complex, requiring a multi-layered integration framework that extends beyond ERP and WMS. In addition to applications required for traditional e-commerce, MLM needs bi-directional API integration with dedicated MLM back-office software, which comes with the following features:
Genealogy Tracking System: When a product is shipped, it’s aligned to the primary salesperson with its upline as a contributor too.
Compensation and Commission Engines: As per the product PV, the back office must distribute the shipped product’s compensation.
Distributor Back-Office Portal: It’s equally important for the company and its distributors to know the shipped product status to better cater to the end customers.
MLM shipping systems are bound to integrate with the platform that keeps shipping, sales, and commissions all next to each other.
It’s more important in the MLM shipping system that data synchronization is event-driven and real-time to allow distributors to provide better customer support, maintain compliance, and avoid delayed payouts.
Apart from that, the MLM shipping system must be able to track returns and replacements and sync the data with the MLM back office to pull back commissions in such cases.
Inventory Distribution Topology
Traditional e-commerce shipping follows a centralized or hub-and-spoke inventory model, in which the products are manufactured at one or more facilities and moved to distribution centers. From there, they are directly sent to customers.
When it’s a centralized model, the entire production is placed at a single warehouse, simplifying stock management but leading to longer delivery times. In the hub-and-spoke model, there’s one main warehouse with multiple distributor centers in different regions.
None of the above-mentioned models is followed by modern MLM shipping systems, as distributors completely rewrite the recipe.
Its multi-tiered topology includes central distribution centers, from where it reaches regional nodes, passed to the distributor level, and in some cases, there are consignment nodes as well.
The MLM shipping system employs MEIO (multi-echelon inventory optimization) algorithms to balance stock allocation as per the distributors’ activity and sales.
Unlike an e-commerce shipping system, in addition to warehouse stock, distributor-held stock-keeping units are also calculated in an MLM shipping system.
Inventory synchronization often relies on API-driven integration between WMS, distributor back-office portals, and MLM ERP systems to prevent overselling and running out of stock.
MLM sales experience high fluctuation, as they depend on multiple factors such as distributors' activity, recruitment, and the MLM business-run campaigns. Therefore, the MLM shipping systems have better prediction capabilities than traditional e-commerce ones to manage this fluctuation.
MLM shipping systems come with multi-level demand planning models that account for seasonality, regional distributor density, and hierarchical sales trends.
Carrier Management and Logistics Optimization
In a traditional e-commerce shipping system, the business either has one permanent carrier partner or the partner is selected on a per-order basis.
When it’s on an order-by-order basis, it makes the shipping cost-effective, but it adds complexity. The shipping system gets integrated with the transport management system that selects the carrier by comparing rate cards, transit times, carrier reputation, and service levels.
It also aligns the carrier with the purchaser's priority, whether it’s cost-effectiveness or same-day delivery or any additional requirements.
When it comes to optimization, it is centered on parcel-level delivery efficiency, as inventory only moves from warehouses or fulfillment centers to the customer.
Overall, though the inventory topology is simpler, carrier management is complex due to the individual attention required.
The MLM logistics management and optimization introduce higher complexity as it needs to accommodate both bulk and parcel-level flow across distributors and customers. For that reason, it requires multi-layer carrier orchestration, where carrier management is not limited to an order-by-order basis and can balance bulk shipping with network-wide shipping to numerous distributors.
The MLM shipping system must orchestrate all three flows simultaneously:
Warehouse to Distributor
Warehouse to Customer
Warehouse to Regional Grouping Hub to Distributor/Cluster (Grouped)
So, how does it technically work?
The MLM shipping system needs to be compatible with both the LTL (less-than-truckload) shipping method, where multiple shippers share space in the same delivery vehicle, and FTL (full truckload), where the business books the complete delivery vehicle.
The LTL is suitable when there’s a direct-to-customer shipment or a small distributor order, while the FTL is used for bulk orders placed by distributors.
Besides that, the MLM shipping system also requires dynamic allocation rules, automated load-building algorithms, and cost-benefit calculators.
Regulatory & Compliance Framework
In a traditional e-commerce shipping system, the compliance stack is relatively simpler and focused on financial integrity and customs processing.
While performing e-commerce shipping, one needs to enforce accurate tax rules, implement customer declaration documents, automate commercial invoice generation, and ensure payment compliance by adhering to PCI-DSS standards.
However, the MLM shipping system requires compliance with MLM-specific laws and regulations of multiple jurisdictions, in addition to traditional e-commerce laws. Besides that, there’s a multi-actor regulatory requirement, which makes it mandatory to interlink compliance with both logistics and compensation.
Many jurisdictions require proof of sale validation before releasing commissions to ensure that an actual end-customer purchase has occurred. Therefore, the MLM shipping system must capture delivery confirmations and tie them to genealogy/commission ledgers before the payout is executed. Similarly, the shipping system requires documented audit trails showing that sales are not inventory loading but actual end-customer sales.
Unlike e-commerce, MLM shipping must support forensic-level traceability:
Immutable shipment logs (blockchain or WORM databases) that regulators can audit.
Chain-of-custody records across multi-echelon inventory nodes (corporate → distributor → customer).
Each shipping event is treated as a compliance checkpoint, not just a logistics update.
Importance of the MLM Shipping System
When you are dealing with MLM products, your shipping system is more than a backend logistics function. You must consider it a mission-critical control layer that directly impacts:
Distributor trust
End-customer satisfaction and retention
Compliance validity
Financial accuracy
In network marketing shipping, delivery serves as the trigger point for financial disbursements, authorizing the system to take actions such as attaching proof of sales, releasing commissions, and initiating return or replacement workflows, if applicable.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Commission Validation and Accuracy | Commissions released only after proof of delivery, preventing fake sales and ensuring timely payouts. |
| Regulatory Safeguards | Creates audit trails, immutable logs, and blockchain records to meet global compliance. |
| Financial Integrity and Clawbacks | Automates commission reversals, prevents overpayment, and flags fraud with ML alerts. |
| Distributor Trust and Retention | Real-time tracking, proof-based payouts, and transparent event logs build distributor confidence. |
| Global Scalability | Supports multi-level distribution, cross-border compliance, multi-currency payouts, and regional SLAs. |
Now, let’s check the importance of the MLM shipping system in detail:
1. Commission Validation and Accuracy
Distributor commissions are tied and only released when the actual product delivery to the end customer takes place. This helps the MLM business detect inventory loading or fake delivery activities.
The shipping system enforces the submission of proof of delivery and syncs it with the MLM solution back office, ensuring timely and accurate commission payment.
2.Regulatory Safeguards
Institutions and organizations, such as the US Federal Trade Commission, mandate that commission payouts are based on verifiable product consumption, and not on recruitment, where the MLM shipping system is helpful, as it creates the micro-level audit trails that give detailed reports on each sale made directly to the customer or via a distributor.
Details captured by the direct selling shipping system also help in preparing the earnings claims document, which is a necessary regulatory requirement.
When you handle delivery through the MLM shipping system, every shipping transaction and related activities (order creation, carrier assignment, delivery to the associated distributor, and end-user delivery scan) are time-stamped, immutable, and reconciled with the MLM back office.
To further strengthen compliance, modern MLM shipping system architecture uses distributed ledger technology (DLT) or blockchain-based event logging, preventing tampering or retroactive manipulation.
By integrating controls to cater to regulations from multiple jurisdictions at the shipping layer, the system ensures that downstream commission settlements are compliant across international markets.
3. Financial Integrity and Clawbacks
In the case of returns/refunds, the system automatically triggers commission clawback workflows, maintaining financial integrity and preventing overpayment. When the clawback workflow is triggered, each return/replacement is logged into the general ledger with dual entries: reversal of commission paid and reallocation of product revenue.
The reversal of commission occurs in a sequence across multiple hierarchical levels, i.e., the distributor who sold the product and its upline. Manually performing the reversal becomes even more challenging in such cases. An MLM shipping system recalculates multi-echelon payout trees and initiates clawback accordingly.
A robust integration between the MLM shipping system and the MLM management tool facilitates the reversal of all dependent uplines’ overrides, including rank achievements, bonuses, etc.
Network marketing shipping systems with machine learning modules can generate alerts when specific distributors or particular geographies have abnormally high return ratios. When integrated with fraud detection engines, it helps MLM businesses mitigate systemic abuse.
When a network marketing shipping system is implemented and has real-time sync with commission engines and accounting software, it ensures zero-latency adjustments, reducing the risk of bad debt accumulation.
4. Distributor Trust and Retention
MLM shipping system’s end-to-end visibility through real-time tracking links connects logistics transparency to financial reliability. The ability to link with multi-carrier APIs allows a distributor to get granular shipment updates at every transit checkpoint, not only for themselves but for their downline as well.
Delivery-related disputes can be handled with proof, safeguarding the trust within the network.
When the shipment is directly sent to the end customer via a distributor’s purchase link, the shipment-event-driven trigger acts as proof of delivery, and the MLM back office takes the action of commission payout.
When the delivery system comes with immutable event logs, accessible by both distributors and your support team, they get an auditable timeline of events, showing everything about “what happened and why.”
Whenever any system anomalies are detected, the system automatically initiates exception workflows to avoid any loss to the distributor as well as the business.
By embedding logistics-to-financial synchronization, distributors gain confidence that earnings will be released on time, every time, provided that shipping milestones are met.
5. Global Scalability
The MLM delivery system facilitates hierarchical distribution models with as many levels as you want, from manufacturing plants to shipping warehouses, from where the products are shipped to national warehouses of various target countries. It is then shipped to regional distribution centers and further to local distribution centers. With the MLM delivery system, you can efficiently track product movement within the hierarchical order.
Using advanced predictive analytics, the system calculates reorder points and stock level requirements per geography, ensuring that optimum levels are maintained at various national distribution centers. It’s based on the number of distributors, their average order value, and end-customer sales.
The MLM delivery system has built-in cross-border taxation and compliance automation tools for computing VAT and other tax forms in real time and customs duties.
Compliance modules enforce jurisdiction-specific MLM rules and also maintain audit-ready transaction logs for a specific jurisdiction, mapping every delivery from manufacturing to the end-customer delivery.
The delivery system aligns with regional service-level agreement frameworks and fulfills regional expectations by monitoring every shipment, switching carriers when needed, and changing routing methods.
To scale across the globe, the MLM delivery system supports multi-currency settlements with automated forex conversions. This helps in providing commissions in the local currency.
When you truly want to connect with the various regional audiences, language-specific shipping documentation comes in handy.
Types of MLM Shipping Models
Now, as we know about the importance of the MLM shipping system, it’s time to look into how the MLM system works according to its different types and where they are applicable. The network marketing shipping system functions through a multilayered supply chain structure, where specialized modules are integrated to optimize the order fulfillment process. These are designed to handle:
Multi-tiered distribution networks
Commission-linked deliveries
Inventory ownership transfers
Now, let’s check each MLM shipping model in detail.
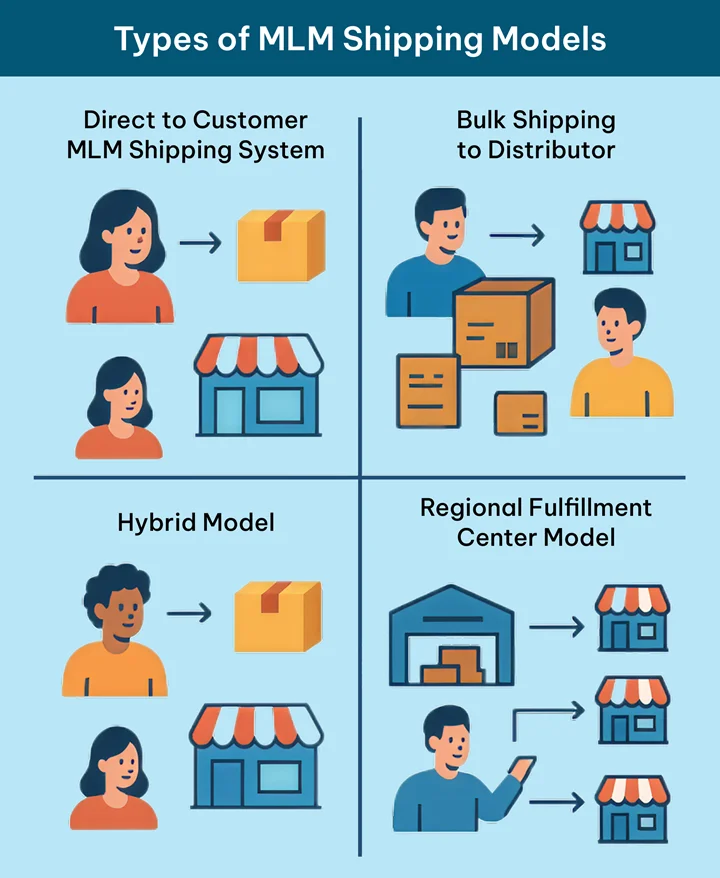
Direct-to-Customer MLM Shipping System
When an MLM entity wants to have centralized control of the inventory despite working through a network of distributors, this model is implemented. In this, distributors place orders on behalf of customers. The distributor request is directly routed to the warehouse or fulfillment center. The product is then shipped to the end customer.
The distributor’s unique ID is tagged to the transaction so that it can be linked to their commission calculation, or if there are any return or replacement requests.
Bulk Shipping to Distributor
When an MLM business doesn’t require centralized control over individual orders, this model is implemented. Rather than tracking each order, the MLM entity tracks the bulk orders made by distributors. Once these orders reach distributors, they can handle the shipment and local sales on their own.
Bulk shipping to distributors helps businesses create a decentralized fulfillment structure where distributors maintain physical stock. It helps businesses reduce operational costs at the entity level and transfer them to distributors. The faster same-day local delivery acts as the cherry on the cake.
However, to ensure compliance while using this MLM shipping system, distributors need to submit proof of delivery, which can be a sales receipt.
Hybrid Model
Many MLM businesses choose to go forward with a hybrid delivery structure that allows them to fulfill direct-to-customer requests as well as bulk procurement by distributors.
Though having two delivery models can increase complexity, it benefits the business with better flexibility and scalability.
For instance, if an MLM business follows a hybrid model, it helps distributors with taking international orders on behalf of the company without needing a physical presence. However, if it’s expensive to ship individual orders for a specific geographic area, bulk shipping proves to be cost-effective.
Similarly, if an MLM business wants to provide flexibility to distributors in how they want to engage with the business, a hybrid model is suitable. It attracts both types of distributors, the ones who want to handle shipping on their own and don’t want to wait for payouts, and others who want to focus on communication, and the business takes care of the shipping.
Regional Fulfillment Center Model
The regional fulfillment center model is usually combined with one or the other delivery model, where the MLM business ships the products to regional centers instead of sending them directly to customers or distributors.
Here, inventory is positioned closer to demand centers, making the overall shipping process faster and quicker.
This is useful for large MLM businesses that have distribution centers across various countries, but manufacturing is focused in one region. So, rather than shipping a single item or bulk orders by one distributor, they ship the entire consignment.
From there, all products are shipped to customers or distributors. This not only saves cost but also takes care of order-related compliance requirements in one go.
Technology in MLM Shipping
It is essential to put the latest, cutting-edge tech to use for the MLM shipping system. It requires integration with multiple tools, must have advanced analytics capabilities, top-notch in-built compliance and a red flag alert system, and tools for an improved user experience. Let’s discuss each one in detail:
Core Integrations Required: Your network marketing shipping system must integrate with the ERP system, MLM back-office software, warehouse management system, order management system, and transport management system to facilitate data synchronization and real-time capabilities.
Multi-Carrier API functionality: Smart automation algorithms for dynamic carrier selection based on geography, pricing, delivery time, and other essential factors.
Routing Algorithm: Make the best use of AI/ML models for dynamic route optimization, reducing delivery times and costs in last-mile and regional cluster shipments.
RFID Tags: Smart RFID tags for real-time visibility of inventory movement, whether the delivery is direct to customers, distributors, or regional centers.
Audit Trail Generation: Utilizes distributed ledger tech to maintain immutable shipment and commission records that can be audited quickly.
Red Flag Alert System: Whenever there’s a non-compliant activity during the delivery process, such as missed sales receipts, inventory loading, etc., the system automatically generates a red flag that helps MLM businesses to take necessary action.
Analytics and Order Prediction Capabilities: As MLM has quite complex distribution networks, which rely on distributors’ activities, the demand forecast becomes complex, too. Technology in the MLM shipping system should take variable factors such as active distributors, downline creation events, and milestones achieved into consideration to understand the near future distributor activity level and conduct a demand forecast accordingly.
Distributor Portals: Provide distributors with the ability to track each delivery-related attribute, such as its status and associated commission. Distributors should also be able to view the complete customer lifecycle to run targeted campaigns and maximize benefits.
Fraud Detection Model: Detect unusual patterns, identify fake orders, bulk returns, and commission manipulations to avoid business exploitation.
Key Takeaways
It’s essential to have one of the best MLM shipping systems in place, as it’s not only for managing logistics. It’s way more than that. It’s the trigger system to facilitate payouts. It’s a part of compliance that validates sales authenticity. It’s a barrier against fraudulent earnings.
When you utilize the MLM shipping system effectively, it becomes a powerful tool to transform complex deliveries into seamless, transparent processes, helping you gain the trust of both distributors and customers alike.
FAQs
1. Why is a dedicated shipping system important for MLM businesses?
It is essential to have a dedicated shipping system for MLM businesses to handle a multi-tiered delivery network. When integrated with necessary tools, such as the MLM back-office, accounting system, and warehouse management system, it can be used to track sales in real-time, confirm and initiate distributor payment, and also take care of compliance.
2. Can MLM shipping systems integrate with MLM software?
Yes, it’s possible to do MLM shipping integration with MLM software such as Global MLM software, using a two-way API. You can connect the solutions to sync the required data and automate commission tracking and payouts for distributors and their upline.
3. How do MLM shipping systems improve distributor satisfaction?
With the MLM shipping system in place, distributors can track the product delivery, support end-customers better, track their payouts, and overall gain a better experience while working with the MLM business.
4. Can MLM shipping systems handle international deliveries?
Yes, robust MLM shipping systems can handle international shipments by understanding the forecast, complying with the jurisdiction-specific MLM laws, calculating the cross-border duties and taxes, and tracking the shipment in real time.
Disclaimer: Global MLM Software do not endorse any companies or products mentioned in this article. The content is derived from publicly available resources and does not favor any specific organizations, individuals or products.