Multi-level marketing (MLM) and direct selling businesses are subject to heightened scrutiny by government agencies to ensure they do not operate as illegal pyramid schemes.
While there is no single dedicated act that governs MLM businesses, they must comply with multiple MLM laws and regulations.
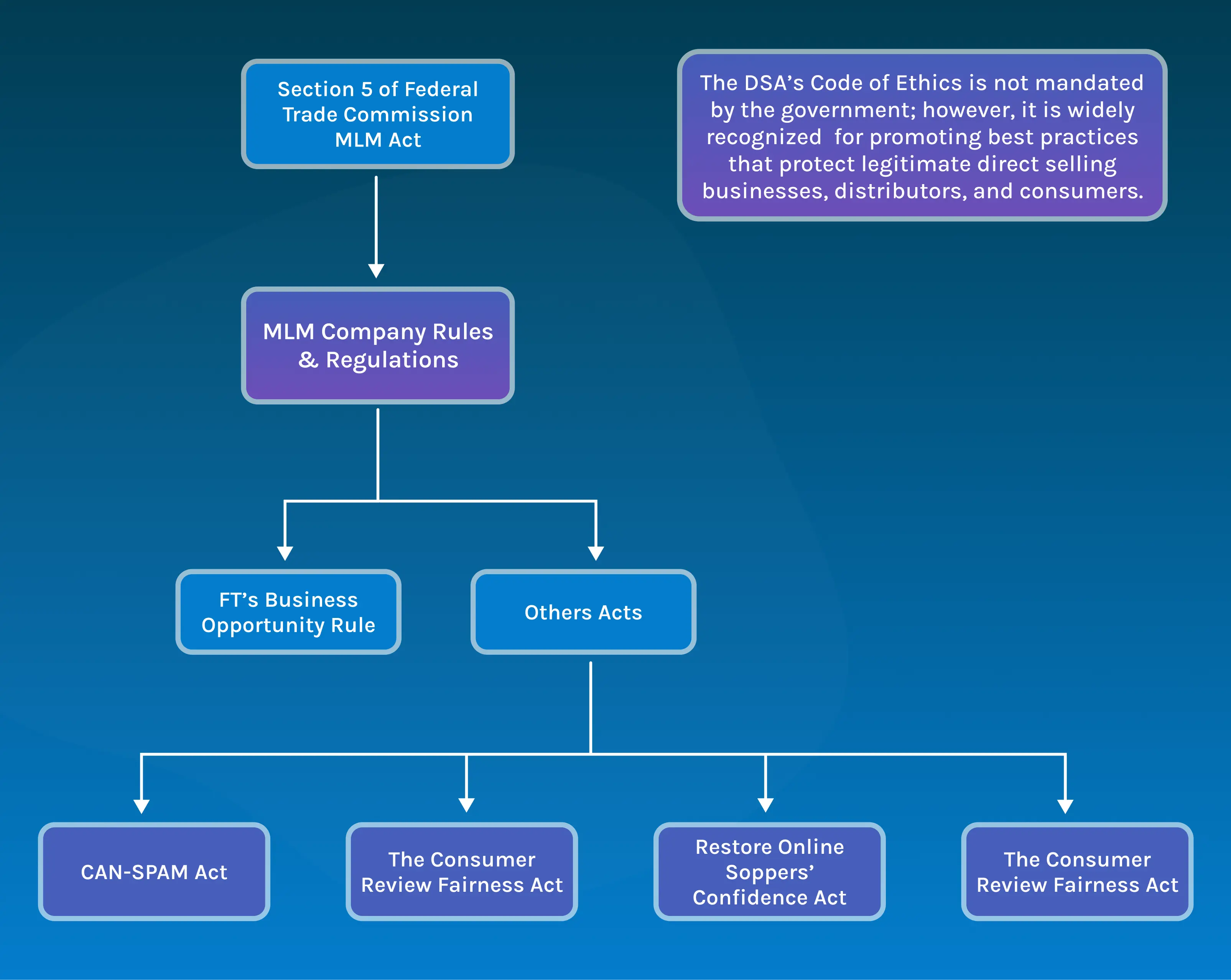
The infographic above highlights these key acts. Let’s briefly discuss each one:
Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act: This is the primary act under which the government regulates MLM business practices. The FTC has issued specific guidance for MLM companies to help them stay compliant and avoid being classified as illegal pyramid schemes. The act prohibits “unfair methods of competition” and “unfair or deceptive acts or practices” that affect commerce.
FTC’s Business Opportunity Rule: This rule is applicable to MLM businesses that sell or offer a business opportunity, require upfront payment, and promise to help the distributor start the business. The Business Opportunity Rule has some additional guidelines, such as disclosing the territorial exclusivity and providing reference details.
CAN-SPAM Act: The CAN-SPAM Act applies to MLM businesses and their distributors if they send commercial emails to their end customers. The customers must be provided with the direct subject line, clearly indicating that it’s promotional content. MLM company rules and regulations require these businesses to provide an easy option to unsubscribe and fulfill the opt-out request promptly.
The Consumer Review Fairness Act: This act protects customers’ right to share honest reviews about the products or services offered by the MLM business. MLM businesses are not allowed to have a non-disparagement clause in contracts to silence negative feedback.
Restore Online Shoppers’ Confidence Act: This act prevents MLM companies that run e-commerce sites to sell their products or services from using deceptive post-transaction practices. Under this act, the MLM companies must obtain clear consent for any additional charges or subscriptions. Sellers must disclose terms upfront and obtain express informed consent before billing.
DSA’s Code of Ethics: The Direct Selling Association’s (DSA) Code of Ethics isn’t a government law but an industry standard. It outlines ethical business practices that member-direct selling companies must follow. These codes of ethics are introduced to protect consumers and salespeople from deceptive conduct. It covers truthful product claims, transparent compensation, fair treatment, and proper income representations, promoting responsible direct selling. Overall, it helps businesses to comply with the FTC’s guidelines as well.

